Why is it so important?
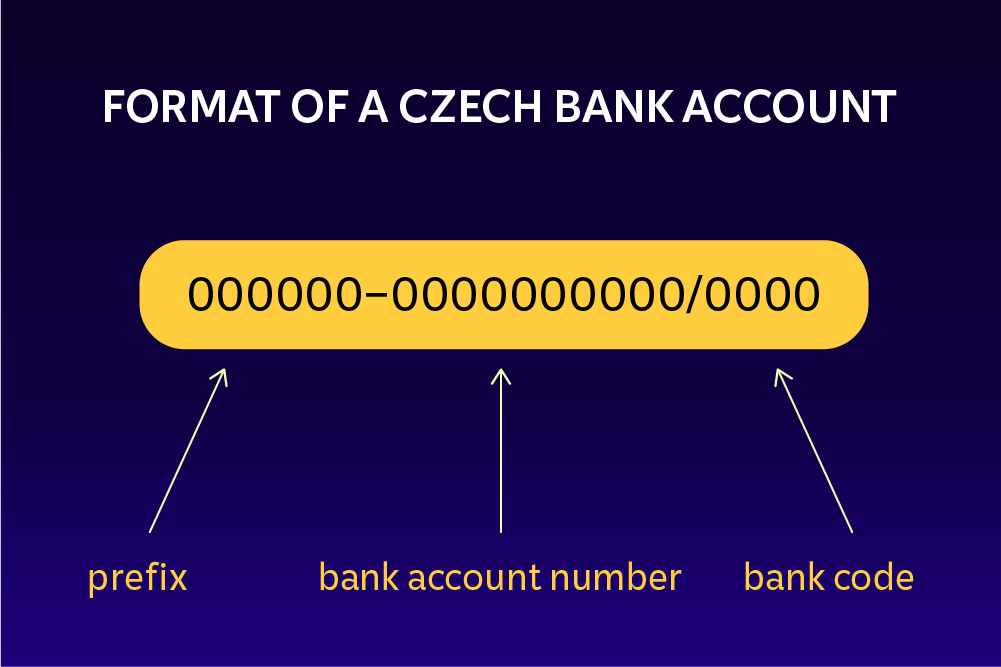
- Bank accounts in the Czech Republic have a specific format, which means that they differ significantly, for example, from Polish bank accounts (see: Format of a Czech bank account).
- Keeping a Polish bank account would be disadvantageous for your Czech customers, as cross-border payments involve additional fees.
- Another disadvantage is the currency conversion from PLN to CZK, which means that the customer will not receive the exact amount in CZK on their Czech bank account. Of course, in Poland it is possible to open a foreign currency account directly in CZK and make transfers from it, but this also involves fees for you, as such a transfer is still considered an international payment.
- A bank transfer is a popular payment method in online stores.
- A bank account in the Czech Republic is necessary for sending financial compensation, for example in the case of a complaint, but mainly for refunding money due to an overpayment on the customer’s side or the customer’s right to withdraw from the contract.
Format of a Czech bank account
The prefix is the first six digits before the dash. It is optional and not every bank account has one. Most bank accounts do not include a prefix.
The account number itself must contain at least 2 digits and no more than 10. In some banks, you can even choose this part of the number yourself. A bank account usually consists of 10 digits.
The last part of the bank account number, after the slash, contains the code of your bank. The bank code is a four-digit number used to directly identify a banking institution in the Czech Republic. The four-digit bank code is used for domestic cashless payments. For payments to Europe or elsewhere in the world, the bank code is not used, but instead the IBAN number is applied.